Freefall - calculating g¶
Equation for calculating acceleration due to gravity is:
where \(g\) is the acceleration due to gravity, \(v1\) is the velocity in gate 1, \(v2\) is the velocity in gate 2 and \(\Delta t\) is the time between gates.
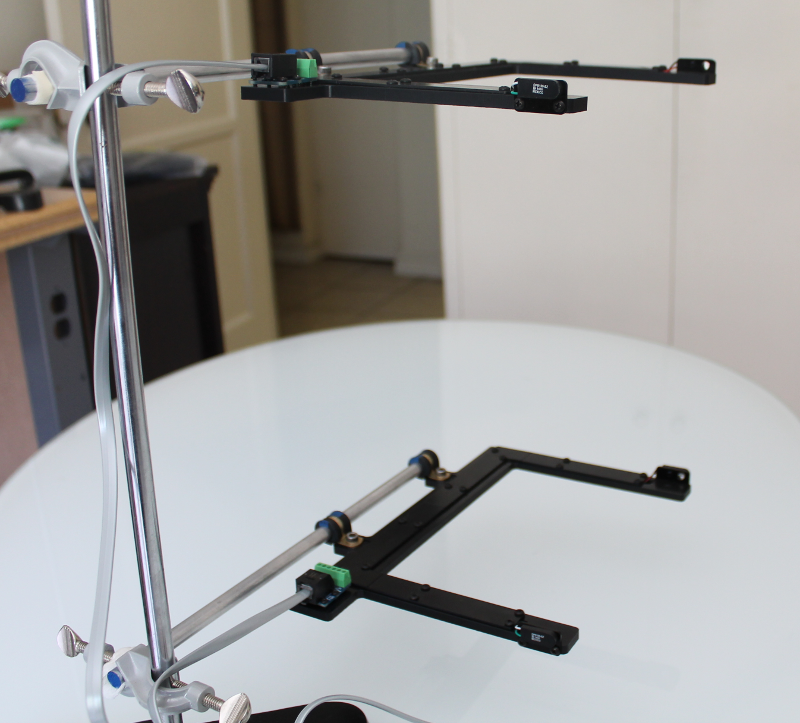
1) Setting up the photogates¶
On a single support stand [1], place the two photogates a distance apart. Make sure that the top (first) photogate is connected to the Photogate 1 position on the Arduino Shield.

2) Software¶
Set-up the software as described in the previous section Using the photogate software.
3) Sample data¶
In the example shown below, we used a 0.5” wide metal block (12.7mm). Hold the object slightly above the first photogate and release to drop it between the two gates. Save data for analysis.
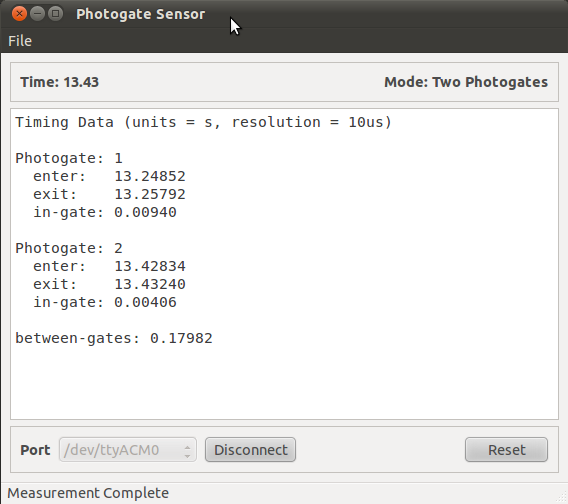
4) Data analysis¶
From time in gates, calculate velocity, \(v\), of falling object:
- \(v\) = object length (m) / time in gate (s)
- \(v1\) = 0.0127/0.00940 = 1.351 \(\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{s}\)
- \(v2\) = 0.0127/0.00406 = 3.128 \(\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{s}\)
From equation, g is given by:
Footnotes
| [1] | Additional equipment from Carolina Biologicals. Support Stand $15.50, Part # 707146 and Clamp Holder, $9.90, Part # 707310 |
